Rwanda’s Agricultural Transformation: A Model for Progress
Discover how Rwanda’s agricultural revolution transforms exports, improves farmer incomes, and ensures food security through modern tea farming, greenhouse technologies, and climate-smart practices. Learn how innovation and sustainability are driving progress.
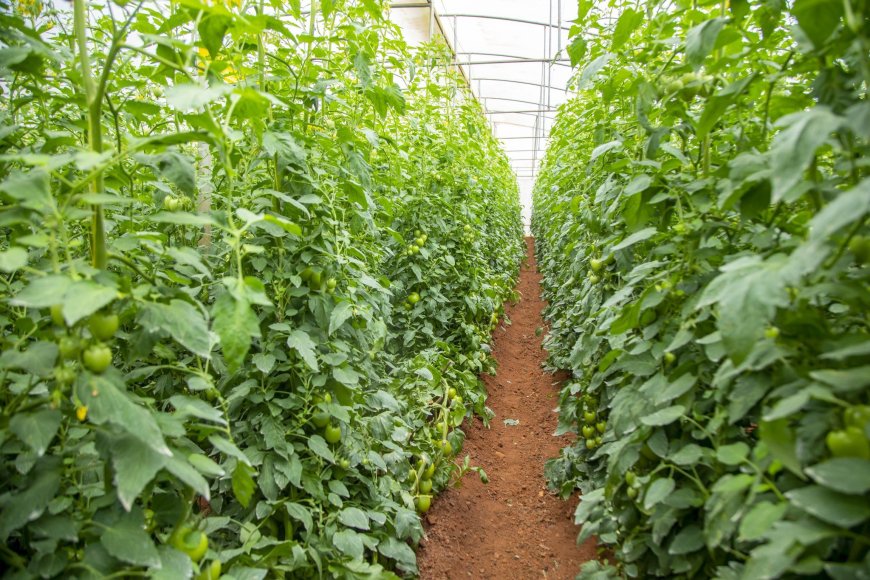

Rwanda’s agricultural sector is undergoing significant transformations driven by innovation, sustainability, and strategic investments. The country is increasing exports, improving farmer incomes, and ensuring food security through advancements like modern tea farming, greenhouse techniques, and climate-smart methodologies. Here is how Rwanda leads in agricultural innovation:
Rwanda’s tea estates are evolving with precision agriculture and mechanization, boosting yield and quality. Tea farmers are growing more valuable crops that meet international standards by adopting contemporary farming techniques. This change is improving Rwanda’s tea exports and significantly raising the income for smallholder farmers.
2. Greenhouse Farming: Year-Round Production and Food Security.

Greenhouse farming is growing swiftly throughout Rwanda, allowing for all-year cultivation of fruits and vegetables. This technique shields crops from harsh weather and pests, resulting in consistent yields and lowering post-harvest losses. By enhancing food security and ensuring high-quality produce, greenhouses are establishing themselves as a key element of Rwanda’s agricultural achievement.
3. Climate-Smart Agriculture: Adapting to a Changing Climate
As weather patterns shift, climate-smart agriculture is increasingly vital. Farmers in Rwanda are embracing conservation farming, agroforestry, and various sustainable techniques to safeguard soil and water resources. These approaches boost resilience and secure ongoing productivity against climate challenges.
4. Crop and Livestock Insurance: Reducing Risks for Farmers
Rwanda has insured 33,628.68 hectares of crops and 51,231 cows to protect farmers from climate shocks and pests. The initiative creates a safety net that encourages investment in better breeds, animal health, and modern farming methods by offering crop and livestock insurance. This empowers smallholder farmers to take risks and innovate confidently without worrying about losing their livelihoods.
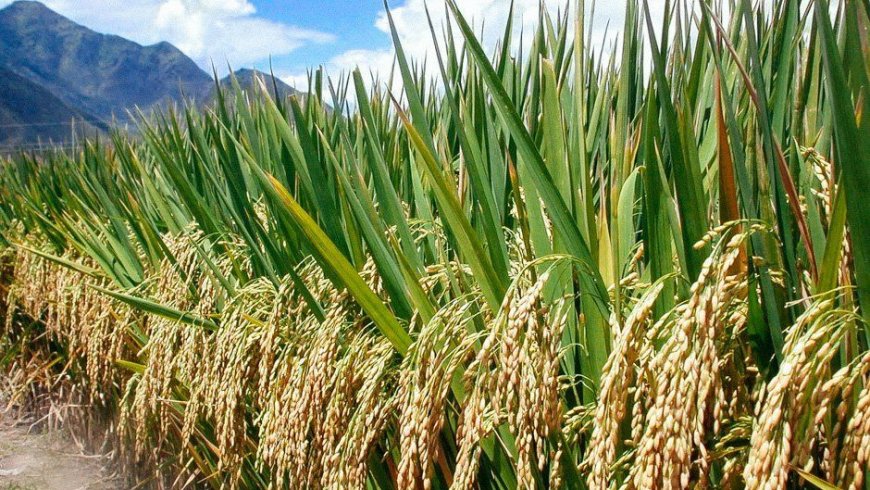

5. Smart Irrigation: Mitigating Drought Effects
The government is promoting innovative irrigation systems to enhance water efficiency and tackle drought challenges. These advanced technologies enable accurate water delivery to crops, optimizing usage and reducing waste. By utilizing techniques such as drip irrigation and soil moisture sensors, farmers can maintain crop production even during dry spells. This method conserves valuable water resources and is crucial for food security. As a result, farmers can secure stable incomes, vital for the economic health of agricultural communities and the broader economy.
6. Modernizing Tea Processing: Adding Value to Exports.
Rwanda’s tea processing sector is upgrading to align with international standards, enhancing the value of raw tea leaves. This enhancement boosts profits for tea farmers and reinforces Rwanda’s standing in the global tea market.
7. Digital Solutions: Empowering Farmers with Technology
Digital tools are transforming agriculture in Rwanda. Mobile applications offer farmers immediate access to weather updates, market prices, and advisory services, enabling them to make well-informed decisions. These digital resources are connecting farmers with markets, improving productivity and profitability.
8. Climate-Resilient Seeds: Ensuring Stable Yields
The distribution of drought-resistant and disease-resistant seeds is helping farmers sustain production levels despite climatic challenges. These resilient varieties are transformative for food security and farmers' livelihoods.
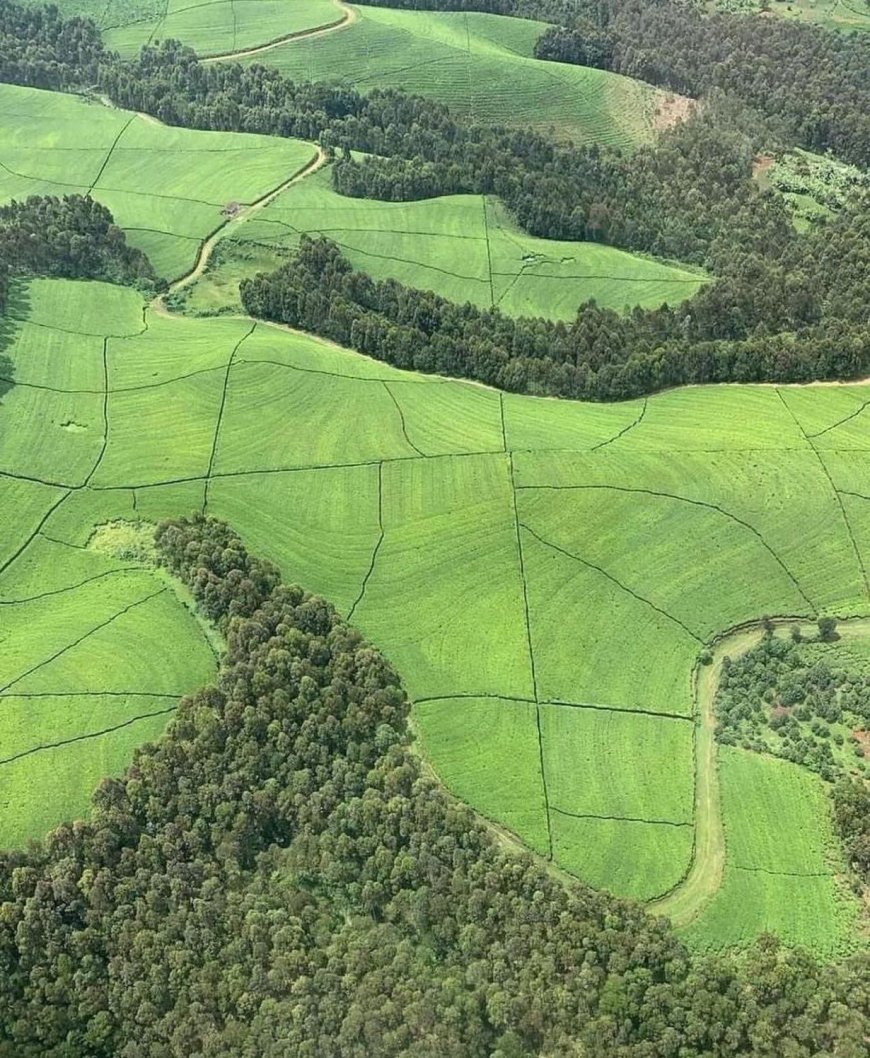

9. Cooperatives: Strengthening Farmer Productivity
Agricultural cooperatives are crucial to the success of farming in Rwanda, serving as a foundation for the agricultural sector. They provide various essential services to smallholder farmers, including training programs that improve farming techniques and promote sustainable practices. Additionally, these cooperatives offer vital agricultural inputs—such as seeds, fertilizers, and tools—at lower prices, enhancing overall farm productivity. Through collective bargaining, they empower farmers by amplifying their voice in the marketplace, allowing them to negotiate better prices for their products and access wider, more profitable markets. This collaborative strategy not only bolsters individual farmers' livelihoods but also promotes economic development in Rwanda's rural areas, fostering community resilience and growth.
10. Precision Farming: Optimizing Resource Use
In recent years, large-scale farmers have been increasingly adopting precision farming techniques to enhance their agricultural practices significantly. This innovative approach involves the use of advanced technologies, such as drones and sensors, which play a crucial role in monitoring crop health and assessing field conditions in real time. By gathering detailed data about soil moisture, nutrient levels, and crop development, farmers can make more informed decisions regarding resource allocation.
Moreover, precision farming allows for optimizing inputs like water, fertilizers, and pesticides. As a result, this technology-driven strategy not only maximizes agricultural yields but also minimizes environmental impact, promoting sustainable farming practices. Ultimately, the integration of these precision tools marks a transformative shift in modern agriculture, leading to more efficient and responsible farming methods that can be essential for addressing the ever-growing global food demands.
11. Sustainable Livestock Farming: Reducing Emissions
Enhanced feeding strategies and sustainable livestock farming techniques are decreasing methane emissions while boosting productivity. These methods not only minimize environmental effects but also enhance the quality and quantity of dairy and meat production.
12. Public-Private Partnerships: Driving Investment
Collaboration between the government and the private sector is playing a vital role in the advancement of infrastructure development, improving market access, and fostering innovation within the agricultural sector. These strategic partnerships are not only enhancing production efficiency but are also crucial to the overall transformation of agriculture in Rwanda. By working together, these entities are creating synergies that lead to improved agricultural practices, better supply chains, and increased opportunities for farmers, ultimately driving economic growth and sustainability across the nation.
13. Youth Involvement: The Future of Agribusiness
Government policies and training programs are encouraging youth to engage in agribusiness. Rwanda is building a new generation of agricultural leaders by equipping young farmers with modern techniques and entrepreneurial skills.
14. Soil Health: A Foundation for Sustainability
Soil health programs that promote the use of organic fertilizers and composting are playing a critical role in ensuring long-term agricultural productivity. These initiatives focus on building and maintaining healthy soils, which are essential for sustainable farming practices. Healthy soils enhance crop yields and contribute to food security by ensuring a consistent supply of nutritious food for growing populations. Moreover, they play a vital role in environmental conservation, helping mitigate climate change's effects, improving water retention, and fostering biodiversity. Investing in soil health through organic methods supports the economy and the ecosystem, creating a more resilient agricultural system that can withstand future challenges.
Rwanda’s Agricultural Transformation: A Model for Progress
Rwanda is transforming agriculture by strongly focusing on innovation, sustainability, and empowering farmers. By adopting advanced technologies, implementing climate-smart practices, and forging strategic partnerships, the nation is enhancing food security, increasing exports, and uplifting livelihoods.
As Rwanda spearheads agricultural innovation, its achievements inspire other countries working to revitalize their agricultural sectors. The prospects for agriculture in Rwanda are promising, with the progress already showing tangible results.
 Kinyarwanda
Kinyarwanda
 English
English








































































